While gonorrhea is a curable STD, it often goes unnoticed, as it does not always exhibit symptoms– especially in women, and can lead to other more serious problems if it’s not treated right away.
Prevalence of Gonorrhea
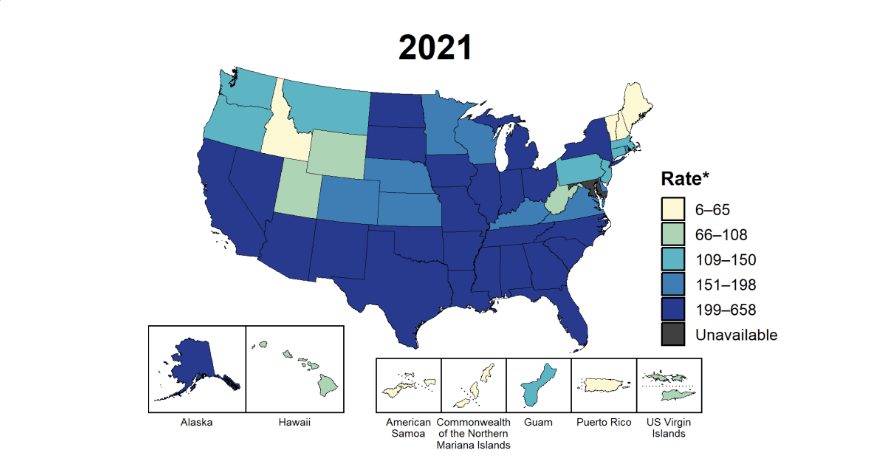
Map Courtesy of CDC. Stats from January 1st, 2014.
Gonorrhea is the second most common STD in the world, with chlamydia taking the number one spot. The latest worldwide data from the World Health Organization states that 62 million people contract gonorrhea every year. That’s the equivalent of the entire population of the United Kingdom. Since 2012, gonorrhea rates in the United States have risen 4.1%. The age ranges who make up the largest percent of gonorrhea cases in the U.S.A. are young men and women from ages 20-24. Infection rates vary greatly by state, as seen on the map above.
Bacterial Infection
Probably the most misspelled STD of all time, gonorrhea is also often referred to as the clap or the drip, due to the discharge that many men experience when infected with this highly contagious bacteria. Caused by the neisseria gonnorhoae bacteria, gonorrhea is passed to partners through unprotected vaginal, oral and anal contact, sometimes even after one unsafe encounter with an infected person.
Not only does gonorrhea affect the area of the body which made contact with the infected partner, this harmful bacteria can also travel to areas of the body such as joints, the heart valves and the eyes and cause serious damage. People with untreated gonorrhea are also more likely to contract HIV or chlamydia while they have this bacteria in their system, which can lead to pelvic inflammatory disorder, ectopic pregnancy and infertility. A startling 47% of people who test positive for gonorrhea also test positive for chlamydia. Pregnant women can pass along gonorrhea to their infants during birth, who will have to be treated for it directly after birth.
Genital, Anal and Oral Symptoms

The most common symptoms of gonorrhea for male genitalia are: swollen and painful testes, discharge from the urethra that is white, green or yellow, and burning during urination. For females, symptoms are often more mild or nonexistent, with up to 50% of women reporting no symptoms at all, but can include: breakthrough bleeding, increased vaginal discharge or pain and burning during urination.
Symptoms of anal gonorrhea can include the following: anal bleeding, pain during bowel movements, anal discharge, general soreness or itchiness. Oral gonorrhea, or gonorrhea of the throat, has symptoms such as white or yellow discharge, sore throat, strep-like symptoms and difficulty swallowing while eating or drinking. Gonorrhea is very easily spread, regardless whether or not you are on the giving or receiving end of things.
Testing and Treatment Options

There is still a myth that males need to have their urethra’s swabbed in order to be tested for a bacterial infection. This is an outdated practice, which hasn’t been the norm in Western medicine for years. In reality, testing is very simple, and in some cases is even free of charge. Find out if you have a local free clinic run by your county or call your primary care physician and ask them where the closet free clinic to you is located.
All that will be needed from you is about 10 minutes of your time, a vial of blood and a urine sample. Occasionally a throat culture will be taken to rule out tonsillitis or strep. Test results typically take between one and three weeks to return. However, if you are exhibiting symptoms, or you have been made aware that your partner was tested positive, your doctor may treat you right away before the results come back.
Bacterial infections of all kinds require antibiotic treatment. They will not go away on their own. Gonorrhea, and any subsequent chlamydia that may also be present, can be treated either with a direct injection of antibiotics or with heavy duty antibiotic pills called ceftriaxone. Follow the instructions, including the warnings about avoiding alcohol and direct sunlight.
Antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea has been a concern amongst doctors and patients alike in recent years, and measures have been taken to ensure that all patients receive the right antibiotics for this bacteria. But, if you have any concerns about this, please discuss it in detail with your doctor.
Aftercare and the Waiting Game

Like other bacterial infections, take all of the prescribed medications that your healthcare provider has instructed for you to take. If you are still exhibiting symptoms after completing your medicine, revisit your doctor for more testing and medicine.
Like with any STD, it is best to wait until you have clearance from your doctor before you start engage in any sexual activity after treatment. Jumping the gun and participating in sex acts before you are fully treated can pass this bacteria along, and could possibly begin a vicious cycle of passing the bacteria back and forth between you and your partner.
Most physicians recommend having both partners treated simultaneously and refraining from any type of sexual contact until the bacteria is known to have dissipated. In some cases, clinics will give one partner two doses of the medicine in order to bring one home to their partner.
Measures for Prevention
The absolute safest means of avoiding gonorrhea is to practice abstinence. But, the next best thing is to use latex condoms and dental dams every time you have oral, vaginal or anal sex. Using an additional condom-safe lubricant and getting properly fitting condoms will ensure your chances of keeping the condom intact and keeping you and your partner(s) safer.
Whether you are a monogamous couple or an orgy-loving swinger, it is vital to your health to get tested regularly, even if you have no symptoms. The minimum for safety is a once a year full panel STD test. Of course, if you are experiencing any symptoms, or have participated in an unsafe sex act, get tested right away. The faster you act against it, the less damage gonorrhea will do to your body.
