Herpes Simplex Virus most commonly affects the mouth and genital regions of the human body. This virus is caught by having skin-to-skin physical contact with someone who carries herpes.
Many people infected with herpes become asymptomatic over time, yet they are still highly contagious. Even though there may no longer be any visual indication that they are a carrier, the virus is still present and active in their cells, which slough off and can be passed to a partner.
Once this virus enters the body, there is no cure. If you get it, you have it for the rest of your life. There are topical prescription medications to control the outbreaks of herpes, which happen from time to time, but they do not eliminate the virus or keep it from being contagious to others. These outbreaks consist of fever blisters, cold sores and clusters of inflamed papules (a crusty elevation of skin) and vesicles (a liquid filled cavity under the skin).
The Center for Disease Control has been tracking the herpes virus since 1966. Since this time the number of initial doctor’s visits for new herpes patients has gone from to 20,000 a year in 1966 to 250,000 visits during 2011. As these statistics indicate, herpes is on the rise in America.
The CDC estimates that currently 1 in 6 adults under the age of 50 carries the herpes virus. If you suspect you have been exposed to herpes, or you are experiencing your first outbreak, get tested. The good news is, the CDC cites condoms and dental dams as an effective means of protection against herpes.
Open communication and safer sex education is essential to the fight against the spread of herpes. Anyone who has been diagnosed with herpes has a great responsibility to be as safe as possible during sexual activities, which includes kissing and oral, vaginal and anal sex. People who are not carriers of herpes also have a challenge in the sense that they need to be ever vigilant against catching it themselves.
While there are multiple variations of the herpes virus, only two are considered to be STDs. These two infectious strains are known as HSV 1 and HSV 2 (this is an abbreviation for herpes simplex virus). There is a lot of confusion about the difference between these two types of herpes, even by the people who carry the virus themselves. Here’s a breakdown of each type of herpes and a frequently asked question about this lifelong virus.
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV 1)
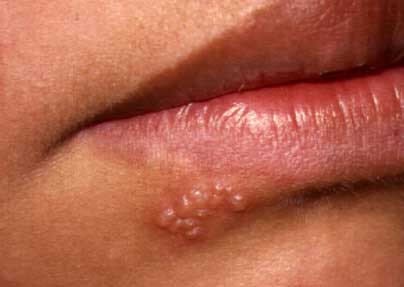
HSV 1 affects the mouth region, including the lips, gums, tongue, throat and the roof of the mouth. Typically, the symptoms appear at the original site of infection anywhere from 3-12 times annually and each painful fluid filled blister takes approximately 2 weeks to heal and disappear. This can lead to a lot of embarrassment for those who frequently have prominent evidence of an STD on their face.
Herpes Simplex Virus 2 (HSV 2)
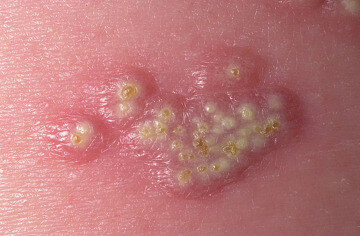
HSV 2 affects the genital region including the penis, scrotum, vagina and anus. HSV 2 is transmitted through contact with shedding skin cells, not bodily fluids. Using a female condom, like the FC2, is the safest way to have sex with a partner who has HSV 2, because it covers a larger area of the skin on the receiving partner than a traditional male condom like the LifeStyles Extra Strength does.
Can Herpes Be Passed From Mouth to Genitals or Vice Versa?
The short answer is yes. If HSV 1 is present in the mouth region it is highly contagious to the genital region. If genitals are infected with HSV 2, this can easily get passed orally and become HSV 1, as well.
There have been debates as to whether or not the HSV 1 strain can cause the HSV 2 strain, but science has definitively proven that indeed it does. In other words, a strain of HSV 1 in the mouth can cause an outbreak by infecting or reinfecting someone if a dental dam or condom isn’t while they perform oral sex, and this can lead to HSV 2.
Similarly, HSV 2 can be spread to the mouth from the genitals during unprotected oral sex. This is why using a condom, like the Trustex Strawberry Flavored Condom or a dental dam is necessary for you and your partner’s protection against Herpes during oral sex. If you are unsure about how to properly use a dental dam for safer oral sex, read more about it in this article entitled ‘How to Use a Dental Dam.’
